The Ultimate Guide to Docking Stations: Components, Manufacturing Processes, and Performance Factors
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of modern computing, the docking station has become a must-have accessory for laptop users. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the heart of docking stations, revealing the intricate components that make them tick, the manufacturing processes that bring them to life, and the factors that influence their performance.
A docking station, often referred to as a port replicator or universal docking station, is a device that enhances the connectivity of a laptop by providing additional ports and interfaces. Whether you’re a power user seeking to expand your workspace or a traveler looking for a convenient way to connect to peripherals on the go, a docking station can be a valuable addition to your setup.
Components of a Docking Station
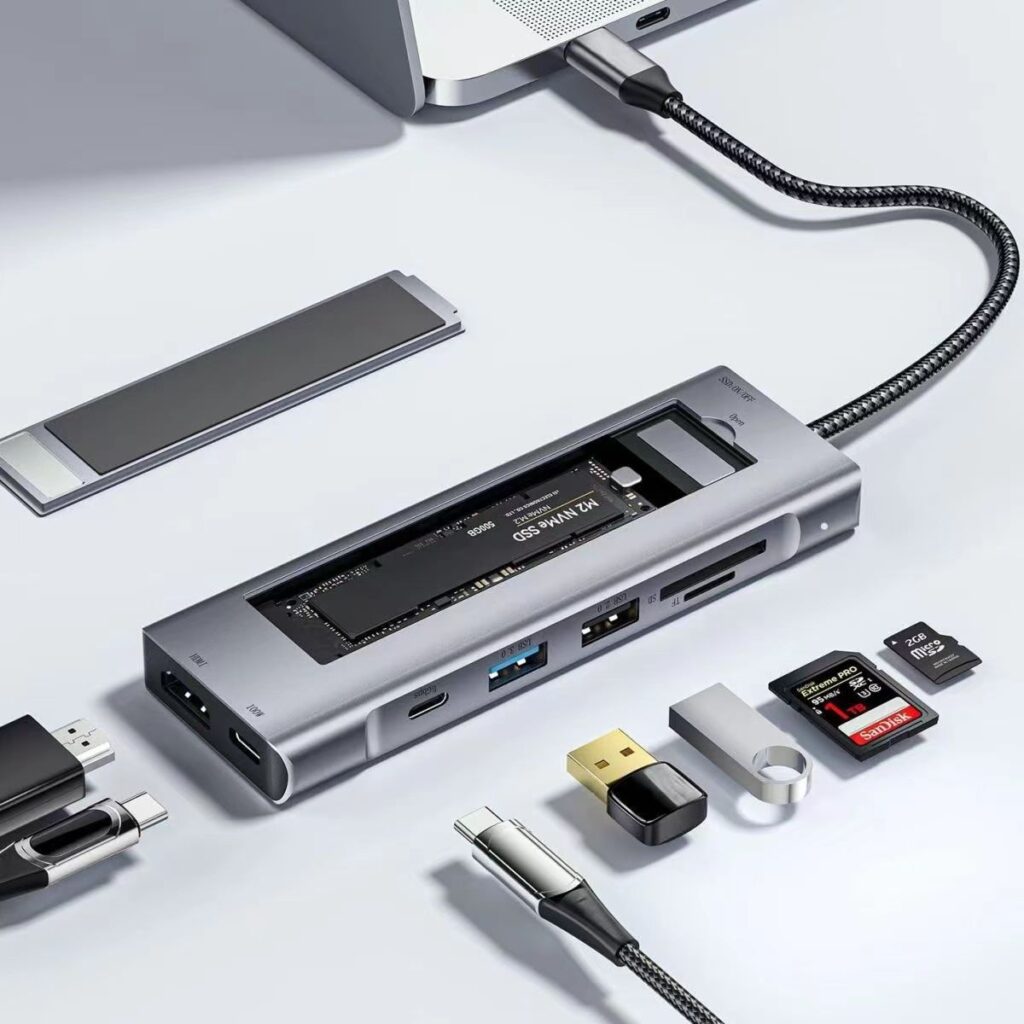
At the core of any docking station, you’ll find a range of components working in harmony to provide seamless connectivity and enhanced functionality. Here’s a breakdown of the key components that make up a docking station:
- Interface Ports
Interface ports are the gateways that allow you to connect various peripherals to your laptop through the docking station. Common port types include:
- USB-A: The traditional USB port, widely used for connecting devices such as keyboards, mice, external hard drives, and printers.
- USB-C: The newer, more versatile USB port that supports higher data transfer speeds and power delivery. Many modern laptops have USB-C ports as their primary interface.
- HDMI and DisplayPort: Used for connecting monitors and displays, enabling you to extend or mirror your laptop’s screen.
- Ethernet (RJ-45): Provides a wired internet connection, often faster and more stable than Wi-Fi.
- Audio Jacks: Allow you to connect external speakers or headphones for improved audio output.
Each port undergoes rigorous testing to ensure compatibility with a wide range of devices and standards.
- Chipset
The chipset is the brains of the docking station, handling data transmission and power management. It ensures smooth communication between your laptop and the connected peripherals. High-quality chipsets from trusted manufacturers are essential for reliable performance.
- Housing
The housing encases the internal components of the docking station, protecting them from dust, dirt, and accidental damage. It also provides structural integrity and ensures the docking station can withstand daily use. Materials such as aluminum and plastic are commonly used for the housing, with each having its own advantages in terms of durability, weight, and heat dissipation.
- Power Supply
The power supply unit converts AC power from the wall outlet to DC power, which is then used to charge and power the connected devices. It’s crucial to have a reliable power supply that can deliver the required voltage and amperage without overheating or causing damage to the connected devices.
- Cables and Connectors
The cables and connectors used in a docking station play a vital role in maintaining a secure and reliable connection between the laptop and the docking station. High-quality cables with sturdy connectors ensure minimal signal loss and maximum durability.
Manufacturing Processes of Docking Station Components
Now let’s delve into the manufacturing processes that bring these components to life. Each component undergoes a series of intricate steps to ensure it meets the highest quality standards.
- Interface Ports
- Material Selection: The raw materials for the ports are carefully selected based on their electrical conductivity, durability, and compatibility with the intended use.
- Machining: The ports undergo precision machining processes such as drilling, cutting, and polishing to achieve the desired shape and size.
- Testing: Each port is tested for electrical conductivity, compatibility with various devices, and durability under extreme conditions.
- Chipset
- Assembly: The individual components of the chipset are assembled using precision techniques to ensure they fit together perfectly.
- Programming: The chipset is programmed with the necessary software and firmware to handle data transmission and power management.
- Quality Control: Rigorous quality control checks are performed to ensure the chipset functions as intended and meets the required specifications.
- Housing
- Material Selection: The housing material is chosen based on its durability, weight, and heat dissipation properties. Aluminum and plastic are common choices.
- Machining: The housing undergoes various machining processes such as milling, drilling, and cutting to achieve the desired shape and size.
- Finishing: The housing is then finished with processes like painting, anodizing, or powder coating to improve its appearance and durability.
- Power Supply
- Component Selection: The components of the power supply unit, such as transformers, capacitors, and rectifiers, are carefully selected based on their electrical properties and reliability.